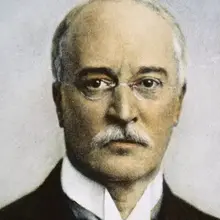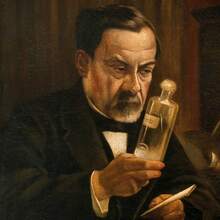Clement VI
1291 - 1352
Pope of the Catholic Church
Clement VI
1291 - 1352
Pope of the Catholic Church
 Vincent de Paul
1581 - 1660
Priest and founder of the Congregation of Mission
Vincent de Paul
1581 - 1660
Priest and founder of the Congregation of Mission
 Daniel Carasso
1905 - 2009
Founder of Danone and Dannon
Daniel Carasso
1905 - 2009
Founder of Danone and Dannon
 Constantine Samuel Rafinesque
1783 - 1840
Botanist and zoologist
Constantine Samuel Rafinesque
1783 - 1840
Botanist and zoologist
 Karl Lagerfeld
1933 - 2019
Creative director of Chanel and Fendi
Karl Lagerfeld
1933 - 2019
Creative director of Chanel and Fendi
 Rudolf Diesel
1858 - 1913
Inventing the diesel engine
Rudolf Diesel
1858 - 1913
Inventing the diesel engine
 Nikolay Muravyov Amursky
1809 - 1881
General admiral
Nikolay Muravyov Amursky
1809 - 1881
General admiral
 Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec
1864 - 1901
Post-Impressionist painter
Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec
1864 - 1901
Post-Impressionist painter
 Antiochus Kantemir
1708 - 1744
poet, diplomat
Antiochus Kantemir
1708 - 1744
poet, diplomat
 Antoine de Saint-Exupery
1900 - 1944
Author of The Little Prince
Antoine de Saint-Exupery
1900 - 1944
Author of The Little Prince
 Konstantin Pobedonostsev
1827 - 1907
Adviser to Alexander II, Alexander III
Konstantin Pobedonostsev
1827 - 1907
Adviser to Alexander II, Alexander III
 Riad al-Turk
1930 - 2024
Syrian opposition leader
Riad al-Turk
1930 - 2024
Syrian opposition leader
 Francois Reichenbach
1921 - 1993
Film director, cinematographer, screenwriter
Francois Reichenbach
1921 - 1993
Film director, cinematographer, screenwriter
 Marguerite of Valois
1553 - 1615
Queen consort of Navarre and France
Marguerite of Valois
1553 - 1615
Queen consort of Navarre and France
 Jacques-Paul Migne
1800 - 1875
Publisher of Patrologia Latina
Jacques-Paul Migne
1800 - 1875
Publisher of Patrologia Latina
 Ali Podrimja
1942 - 2012
Poet and author
Ali Podrimja
1942 - 2012
Poet and author
 Henry IV of France
1553 - 1610
King of France and Navarre
Henry IV of France
1553 - 1610
King of France and Navarre
 Francis II of France
1544 - 1560
King of France and Scotland
Francis II of France
1544 - 1560
King of France and Scotland
 Barbara
1930 - 1997
Singer and songwriter of chanson genre
Barbara
1930 - 1997
Singer and songwriter of chanson genre
 Aziz Sedky
1920 - 2008
Prime Minister of Egypt
Aziz Sedky
1920 - 2008
Prime Minister of Egypt
 Niccolo Paganini
1782 - 1840
Violinist
Niccolo Paganini
1782 - 1840
Violinist
 Montesquieu
1689 - 1755
Political philosopher and jurist
Montesquieu
1689 - 1755
Political philosopher and jurist
 Nikolai Bogdanov Belsky
1870 - 1960
Art critic and historian
Nikolai Bogdanov Belsky
1870 - 1960
Art critic and historian
 Yves Congar
1904 - 1995
Theologian and cardinal
Yves Congar
1904 - 1995
Theologian and cardinal
 Barbu Dimitrie Stirbei
1799 - 1869
Prince
Barbu Dimitrie Stirbei
1799 - 1869
Prince
 Oscar Wilde
1854 - 1900
Playwright
Oscar Wilde
1854 - 1900
Playwright
 Coco Chanel
1883 - 1971
Fashion designer and founder of Chanel brand
Coco Chanel
1883 - 1971
Fashion designer and founder of Chanel brand
 Francoise Frenkel
1889 - 1975
Writer and bookseller
Francoise Frenkel
1889 - 1975
Writer and bookseller
 John XXII
1244 - 1334
Pope and theologian
John XXII
1244 - 1334
Pope and theologian
 Frederic Chopin
1810 - 1849
Romantic composer and virtuoso pianist
Frederic Chopin
1810 - 1849
Romantic composer and virtuoso pianist
 Victor Hugo
1802 - 1885
Romantic writer and politician
Victor Hugo
1802 - 1885
Romantic writer and politician
 Louis XVI of France
1754 - 1793
King of France and Navarre, King of the French
Louis XVI of France
1754 - 1793
King of France and Navarre, King of the French
 Olga Boznanska
1865 - 1940
Painter
Olga Boznanska
1865 - 1940
Painter
 Jean Gabin
1904 - 1976
Actor and singer
Jean Gabin
1904 - 1976
Actor and singer
 Henri Gregoire
1750 - 1831
Constitutional bishop of Blois
Henri Gregoire
1750 - 1831
Constitutional bishop of Blois
 Jean-Luc Godard
1930 - 2022
Film director, screenwriter, film critic
Jean-Luc Godard
1930 - 2022
Film director, screenwriter, film critic
 Virgil Ierunca
1920 - 2006
Literary critic
Virgil Ierunca
1920 - 2006
Literary critic
 Prince Ali Khan
1911 - 1960
Racehorse owner and diplomat
Prince Ali Khan
1911 - 1960
Racehorse owner and diplomat
 Claude Monet
1840 - 1926
Founder of impressionist painting
Claude Monet
1840 - 1926
Founder of impressionist painting
 Le Corbusier
1887 - 1965
Le Corbusier
1887 - 1965
 Konstantin Somov
1869 - 1939
Russian and French painter
Konstantin Somov
1869 - 1939
Russian and French painter
 Gheorghe Bibescu
1804 - 1873
Prince
Gheorghe Bibescu
1804 - 1873
Prince
 Bernard of Clairvaux
1090 - 1153
Cistercian monk
Bernard of Clairvaux
1090 - 1153
Cistercian monk
 Clovis I
-466 - 511
King of the Franks
Clovis I
-466 - 511
King of the Franks
 Paul Celan
1920 - 1970
Poet
Paul Celan
1920 - 1970
Poet
 Jacques Offenbach
1819 - 1880
Operetta pioneer
Jacques Offenbach
1819 - 1880
Operetta pioneer
 Celine Arnauld
1885 - 1952
Poet
Celine Arnauld
1885 - 1952
Poet
 Germanus of Auxerre
378 - 445
Bishop of Autissiodorum and defender of orthodoxy
Germanus of Auxerre
378 - 445
Bishop of Autissiodorum and defender of orthodoxy
 Nemir Kirdar
1936 - 2020
Founder and CEO of Investcorp
Nemir Kirdar
1936 - 2020
Founder and CEO of Investcorp
 Michel Kilo
1940 - 2021
writer and human rights activist
Michel Kilo
1940 - 2021
writer and human rights activist
 Louis XIII of France
1601 - 1643
King of France and Navarre
Louis XIII of France
1601 - 1643
King of France and Navarre
 Alberto Cavalcanti
1897 - 1982
Film director and producer
Alberto Cavalcanti
1897 - 1982
Film director and producer
 Raoul Coutard
1924 - 2016
Cinematographer for French New Wave directors
Raoul Coutard
1924 - 2016
Cinematographer for French New Wave directors
 Albert Schweitzer
1875 - 1965
Founder of the Albert Schweitzer Hospital
Albert Schweitzer
1875 - 1965
Founder of the Albert Schweitzer Hospital
 Richard Anthony
1938 - 2015
French pop singer
Richard Anthony
1938 - 2015
French pop singer
 Charles de Foucauld
1858 - 1916
Catholic priest
Charles de Foucauld
1858 - 1916
Catholic priest
 Dodi Fayed
1955 - 1997
Film producer
Dodi Fayed
1955 - 1997
Film producer
 Nicolas Malebranche
1638 - 1715
Rationalist philosopher and theologian
Nicolas Malebranche
1638 - 1715
Rationalist philosopher and theologian
 Sassoon Eskell
1860 - 1932
Deputy for the Iraqi Parliament
Sassoon Eskell
1860 - 1932
Deputy for the Iraqi Parliament
 Pierre Claude Francois Daunou
1761 - 1840
French statesman and historian
Pierre Claude Francois Daunou
1761 - 1840
French statesman and historian
 Lili Damita
1904 - 1994
actress and singer
Lili Damita
1904 - 1994
actress and singer
 Vincent van Gogh
1853 - 1890
Vincent van Gogh
1853 - 1890
 Natalia Goncharova
1881 - 1962
Painter and designer
Natalia Goncharova
1881 - 1962
Painter and designer
 James Stuart
1633 - 1701
King of England, Scotland and Ireland from 1685
James Stuart
1633 - 1701
King of England, Scotland and Ireland from 1685
 France Gall
1947 - 2018
Yé-yé singer and Eurovision winner
France Gall
1947 - 2018
Yé-yé singer and Eurovision winner
 Kim Lefevre
1935 - 2021
Writer, Translator
Kim Lefevre
1935 - 2021
Writer, Translator
 Cecile Aubry
1928 - 2010
Actress, author, television screenwriter
Cecile Aubry
1928 - 2010
Actress, author, television screenwriter
 Georges Guetary
1915 - 1997
Singer, dancer, cabaret performer and film actor
Georges Guetary
1915 - 1997
Singer, dancer, cabaret performer and film actor
 Krzysztof Gawedzki
1947 - 2022
Mathematical physics
Krzysztof Gawedzki
1947 - 2022
Mathematical physics
 Louis II, Cardinal of Guise
1555 - 1588
Cardinal and Archbishop of Reims
Louis II, Cardinal of Guise
1555 - 1588
Cardinal and Archbishop of Reims
 Dom Joseph Pothier
1835 - 1923
Liturgist and musicologist
Dom Joseph Pothier
1835 - 1923
Liturgist and musicologist
 Witold Gombrowicz
1904 - 1969
Novelist, playwright, diarist
Witold Gombrowicz
1904 - 1969
Novelist, playwright, diarist
 Mikhail Larionov
1881 - 1964
Painter and stage designer
Mikhail Larionov
1881 - 1964
Painter and stage designer
 Bernard Maris
1946 - 2015
Economist, writer and journalist
Bernard Maris
1946 - 2015
Economist, writer and journalist
 Nikolaos Sokrates Politis
1872 - 1942
International lawyer, diplomat, scholar
Nikolaos Sokrates Politis
1872 - 1942
International lawyer, diplomat, scholar
 Marie Bonaparte
1882 - 1962
Author and psychoanalyst
Marie Bonaparte
1882 - 1962
Author and psychoanalyst
 Henri de Lubac
1896 - 1991
Theologian and priest
Henri de Lubac
1896 - 1991
Theologian and priest
 Palladius
365 - 457
Bishop of Ireland
Palladius
365 - 457
Bishop of Ireland
 Alexandre Dumas
1802 - 1870
Historical novels and adventure stories
Alexandre Dumas
1802 - 1870
Historical novels and adventure stories
 Hugues Felicite Robert de Lamennais
1782 - 1854
Catholic priest, philosopher
Hugues Felicite Robert de Lamennais
1782 - 1854
Catholic priest, philosopher
 Gerard Debreu
1921 - 2004
Nobel laureate in economics
Gerard Debreu
1921 - 2004
Nobel laureate in economics
 Carlos Reichenbach
1945 - 2012
Film director and producer
Carlos Reichenbach
1945 - 2012
Film director and producer
 Alexandru Proca
1897 - 1955
Physicist
Alexandru Proca
1897 - 1955
Physicist
 Rene-Just Hauy
1743 - 1822
mineralogist and crystallographer
Rene-Just Hauy
1743 - 1822
mineralogist and crystallographer
 Sergiu Celibidache
1912 - 1996
Conductor
Sergiu Celibidache
1912 - 1996
Conductor
 Marguerite Duras
1914 - 1996
novelist
Marguerite Duras
1914 - 1996
novelist
 Luis Ocana
1945 - 1994
Road bicycle racer
Luis Ocana
1945 - 1994
Road bicycle racer
 Bernardino Pinera Carvallo
1915 - 2020
Bishop of Temuco and Archbishop of La Serena
Bernardino Pinera Carvallo
1915 - 2020
Bishop of Temuco and Archbishop of La Serena
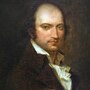 Andre Chenier
1762 - 1794
Poet and political journalist
Andre Chenier
1762 - 1794
Poet and political journalist
 Mai Trung Thu
1906 - 1980
Painter
Mai Trung Thu
1906 - 1980
Painter
 Berenger Sauniere
1852 - 1917
Priest of Rennes-le-Château
Berenger Sauniere
1852 - 1917
Priest of Rennes-le-Château
 Henri Teissier
1929 - 2020
Bishop of Oran and Archbishop of Algiers
Henri Teissier
1929 - 2020
Bishop of Oran and Archbishop of Algiers
 Richard I of England
1157 - 1199
King of England and leader of the Third Crusade
Richard I of England
1157 - 1199
King of England and leader of the Third Crusade
 Francois Clouet
1510 - 1572
Court painter and miniaturist
Francois Clouet
1510 - 1572
Court painter and miniaturist
 Gustave Eiffel
1832 - 1923
Civil engineer and architect
Gustave Eiffel
1832 - 1923
Civil engineer and architect
 Mary of Guise
1515 - 1560
Queen consort and regent of Scotland
Mary of Guise
1515 - 1560
Queen consort and regent of Scotland
 Louis Cappel
1585 - 1658
Protestant churchman and scholar
Louis Cappel
1585 - 1658
Protestant churchman and scholar
 Anatoly Lunacharsky
1875 - 1933
First Soviet People's Commissar of Education
Anatoly Lunacharsky
1875 - 1933
First Soviet People's Commissar of Education
 Josephine Baker
1906 - 1975
Music-hall entertainer and French Resistance agent
Josephine Baker
1906 - 1975
Music-hall entertainer and French Resistance agent
 Jean Orry
1652 - 1719
Controller-General of Finances in Spain
Jean Orry
1652 - 1719
Controller-General of Finances in Spain
 Abdul Halim Khaddam
1932 - 2020
Vice President of Syria
Abdul Halim Khaddam
1932 - 2020
Vice President of Syria
 Louis Aime Augustin Le Prince
1841 - 1890
Inventor of an early motion-picture camera
Louis Aime Augustin Le Prince
1841 - 1890
Inventor of an early motion-picture camera
 Paul Gauguin
1848 - 1903
Painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramist, writer
Paul Gauguin
1848 - 1903
Painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramist, writer
 Andre Truong Trong Thi
1936 - 2005
Computer Engineer
Andre Truong Trong Thi
1936 - 2005
Computer Engineer
 Felix Dupanloup
1802 - 1878
Bishop of Orléans, leader of Liberal Catholicism
Felix Dupanloup
1802 - 1878
Bishop of Orléans, leader of Liberal Catholicism
 Georges Tarabichi
1939 - 2016
Writer, philosopher, and translator
Georges Tarabichi
1939 - 2016
Writer, philosopher, and translator
 Thurstan of Bayeux
1070 - 1140
Archbishop of York
Thurstan of Bayeux
1070 - 1140
Archbishop of York
 Charilaos Trikoupis
1832 - 1896
Prime Minister of Greece
Charilaos Trikoupis
1832 - 1896
Prime Minister of Greece
 John Eudes
1601 - 1680
Founder of the Congregation of Jesus and Mary
John Eudes
1601 - 1680
Founder of the Congregation of Jesus and Mary
 Peter Dmytruk
1920 - 1943
Sergeant in the Royal Canadian Air Force
Peter Dmytruk
1920 - 1943
Sergeant in the Royal Canadian Air Force
 Claude La Colombiere
1641 - 1682
Priest and confessor of Margaret Mary Alacoque
Claude La Colombiere
1641 - 1682
Priest and confessor of Margaret Mary Alacoque
 Isabella of France
1295 - 1358
Queen consort of England and regent of England
Isabella of France
1295 - 1358
Queen consort of England and regent of England
 Oswald Mosley
1896 - 1980
Leader of the British Union of Fascists
Oswald Mosley
1896 - 1980
Leader of the British Union of Fascists
 Felix of Valois
1127 - 1212
Co-founder of the Trinitarian Order
Felix of Valois
1127 - 1212
Co-founder of the Trinitarian Order
 Louis The Pious
778 - 840
Emperor of the Franks
Louis The Pious
778 - 840
Emperor of the Franks
 George V of Hanover
1819 - 1878
King of Hanover
George V of Hanover
1819 - 1878
King of Hanover
 Louise of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg
1800 - 1831
Duchess consort of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld
Louise of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg
1800 - 1831
Duchess consort of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld
 Blaise Pascal
1623 - 1662
Mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher
Blaise Pascal
1623 - 1662
Mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher
 Charles Maurice de Talleyrand
1754 - 1838
French secularized clergyman, statesman
Charles Maurice de Talleyrand
1754 - 1838
French secularized clergyman, statesman
 Marcel Duchamp
1887 - 1968
Painter, sculptor, chess player, writer
Marcel Duchamp
1887 - 1968
Painter, sculptor, chess player, writer
 Jean-Jacques Olier
1608 - 1657
Founder of the Sulpicians
Jean-Jacques Olier
1608 - 1657
Founder of the Sulpicians
 Kieron Moore
1924 - 2007
Film and television actor
Kieron Moore
1924 - 2007
Film and television actor
 Charles William Joseph Emile Le Gendre
1830 - 1899
Army officer and diplomat
Charles William Joseph Emile Le Gendre
1830 - 1899
Army officer and diplomat
 Leon Dehon
1843 - 1925
Founder of the Congregation of the Sacred Heart
Leon Dehon
1843 - 1925
Founder of the Congregation of the Sacred Heart
 Robert Palmer
1949 - 2003
Singer, songwriter, record producer
Robert Palmer
1949 - 2003
Singer, songwriter, record producer
 Claude Debussy
1862 - 1918
Author of The Little Prince
Claude Debussy
1862 - 1918
Author of The Little Prince
 Hugh Capet
940 - 996
King of France, founder of Capetian dynasty
Hugh Capet
940 - 996
King of France, founder of Capetian dynasty
 Georges Nomarski
1919 - 1997
Creator of differential interference microscopy
Georges Nomarski
1919 - 1997
Creator of differential interference microscopy
 Anne Robert Jacques Turgot
1727 - 1781
Comptroller general of finance under Louis XVI
Anne Robert Jacques Turgot
1727 - 1781
Comptroller general of finance under Louis XVI
 Antoine-Augustin Cournot
1801 - 1877
Economist
Antoine-Augustin Cournot
1801 - 1877
Economist
 Louis Rene Edouard de Rohan
1734 - 1803
Bishop of Strasbourg, Grand Almoner of France
Louis Rene Edouard de Rohan
1734 - 1803
Bishop of Strasbourg, Grand Almoner of France
 Grigore Gafencu
1892 - 1957
Diplomat
Grigore Gafencu
1892 - 1957
Diplomat
 Nureddin al-Atassi
1929 - 1992
President of Syria
Nureddin al-Atassi
1929 - 1992
President of Syria
 Samuel Beckett
1906 - 1989
Nobel laureate in literature
Samuel Beckett
1906 - 1989
Nobel laureate in literature
 Jacques Damala
1855 - 1889
Actor and husband of Sarah Bernhardt
Jacques Damala
1855 - 1889
Actor and husband of Sarah Bernhardt
 Constantin Brancusi
1876 - 1957
Sculptor
Constantin Brancusi
1876 - 1957
Sculptor
 Wassily Kandinsky
1866 - 1944
Painter of abstract art
Wassily Kandinsky
1866 - 1944
Painter of abstract art
 Zinaida Serebriakova
1884 - 1967
Russian and French painter
Zinaida Serebriakova
1884 - 1967
Russian and French painter
 Olivia de Havilland
1916 - 2020
Actress of Hollywood’s Golden Age
Olivia de Havilland
1916 - 2020
Actress of Hollywood’s Golden Age
 Pierre-Joseph Proudhon
1809 - 1865
Founder of mutualism and anarchism
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon
1809 - 1865
Founder of mutualism and anarchism
 Henri Alekan
1909 - 2001
Cinematographer of Beauty and the Beast
Henri Alekan
1909 - 2001
Cinematographer of Beauty and the Beast
 Vu Cao Dam
1908 - 2000
Painter, Sculptor
Vu Cao Dam
1908 - 2000
Painter, Sculptor
 Leon Bakst
1866 - 1924
Scene and costume design for the Ballets Russes
Leon Bakst
1866 - 1924
Scene and costume design for the Ballets Russes
 Mihail Kogalniceanu
1817 - 1891
Statesman
Mihail Kogalniceanu
1817 - 1891
Statesman
 Nicolae Titulescu
1882 - 1941
Diplomat
Nicolae Titulescu
1882 - 1941
Diplomat
 Diana Princess of Wales
1961 - 1997
Diana Princess of Wales
1961 - 1997
 Henri Breuil
1877 - 1961
Authority on prehistoric cave art
Henri Breuil
1877 - 1961
Authority on prehistoric cave art
 Charles de Gaulle
1890 - 1970
President of France
Charles de Gaulle
1890 - 1970
President of France
 Albert Camus
1913 - 1960
Existentialist philosopher and novelist
Albert Camus
1913 - 1960
Existentialist philosopher and novelist
 Pierre Cauchon
1371 - 1442
Bishop of Beauvais and judge of Joan of Arc
Pierre Cauchon
1371 - 1442
Bishop of Beauvais and judge of Joan of Arc
We Need -- admin in