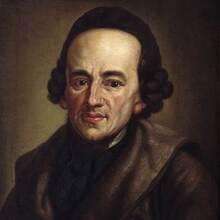Karin Dor
1938 - 2017
Actress in Edgar Wallace, Karl May
Karin Dor
1938 - 2017
Actress in Edgar Wallace, Karl May
 Albrecht Durer
1471 - 1528
Painter and printmaker of the German Renaissance
Albrecht Durer
1471 - 1528
Painter and printmaker of the German Renaissance
 Nwafor Orizu
1914 - 1999
President of the Nigerian Senate
Nwafor Orizu
1914 - 1999
President of the Nigerian Senate
 Carl Philipp Gottfried von Clausewitz
1780 - 1831
Prussian general and military strategist
Carl Philipp Gottfried von Clausewitz
1780 - 1831
Prussian general and military strategist
 Princess Sophie of Greece and Denmark
1914 - 2001
Princess of Hesse-Kassel and Hanover
Princess Sophie of Greece and Denmark
1914 - 2001
Princess of Hesse-Kassel and Hanover
 Carl Friedrich Gauss
1777 - 1855
Mathematics and sciences
Carl Friedrich Gauss
1777 - 1855
Mathematics and sciences
 Johann Christian Bach
1735 - 1782
Composer of the Classical era
Johann Christian Bach
1735 - 1782
Composer of the Classical era
 Karlheinz Bohm
1928 - 2014
actor and founder of Menschen für Menschen
Karlheinz Bohm
1928 - 2014
actor and founder of Menschen für Menschen
 Karl Brandt
1904 - 1948
Personal physician of Adolf Hitler
Karl Brandt
1904 - 1948
Personal physician of Adolf Hitler
 Charles Edward, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
1884 - 1954
Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
Charles Edward, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
1884 - 1954
Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
 Nicole Brown Simpson
1959 - 1994
Actress and Ex-wife of O.J. Simpson
Nicole Brown Simpson
1959 - 1994
Actress and Ex-wife of O.J. Simpson
 Margot Frank
1926 - 1945
Diarist
Margot Frank
1926 - 1945
Diarist
 Konrad Zuse
1910 - 1995
Computer scientist and engineer
Konrad Zuse
1910 - 1995
Computer scientist and engineer
 Richard Wagner
1813 - 1883
Composer of operas and music dramas
Richard Wagner
1813 - 1883
Composer of operas and music dramas
 Leopold I of Belgium
1790 - 1865
King of the Belgians and European diplomat
Leopold I of Belgium
1790 - 1865
King of the Belgians and European diplomat
 Richard Georg Strauss
1864 - 1949
Composer
Richard Georg Strauss
1864 - 1949
Composer
 Charlemagne
747 - 814
Emperor of the Romans and King of the Franks
Charlemagne
747 - 814
Emperor of the Romans and King of the Franks
 Jakob Fugger
1459 - 1525
Mining entrepreneur and financier of the Habsburgs
Jakob Fugger
1459 - 1525
Mining entrepreneur and financier of the Habsburgs
 Martin Niemoller
1892 - 1984
Anti-Nazi activist
Martin Niemoller
1892 - 1984
Anti-Nazi activist
 Louis Ferdinand, Prince of Prussia
1772 - 1806
Soldier and musician
Louis Ferdinand, Prince of Prussia
1772 - 1806
Soldier and musician
 Paul von Hindenburg
1847 - 1934
Field marshal and president of Germany
Paul von Hindenburg
1847 - 1934
Field marshal and president of Germany
 Frederick the Great
1712 - 1786
King of Prussia and military leader
Frederick the Great
1712 - 1786
King of Prussia and military leader
 Adam Weishaupt
1748 - 1830
Founder of the Illuminati
Adam Weishaupt
1748 - 1830
Founder of the Illuminati
 Caroline Herschel
1750 - 1848
Astronomer and comet discoverer
Caroline Herschel
1750 - 1848
Astronomer and comet discoverer
 Fritz Todt
1891 - 1942
Construction engineer and senior Nazi figure
Fritz Todt
1891 - 1942
Construction engineer and senior Nazi figure
 Albrecht Altdorfer
1480 - 1538
Renaissance painter, landscape artist, printmaker
Albrecht Altdorfer
1480 - 1538
Renaissance painter, landscape artist, printmaker
 Herbert von Bismarck
1849 - 1904
Foreign Secretary of Germany
Herbert von Bismarck
1849 - 1904
Foreign Secretary of Germany
 Josef Mengele
1911 - 1979
Nazi physician and SS officer at Auschwitz
Josef Mengele
1911 - 1979
Nazi physician and SS officer at Auschwitz
 Ernst Barlach
1870 - 1938
Expressionist sculptor and writer
Ernst Barlach
1870 - 1938
Expressionist sculptor and writer
 Radius Prawiro
1928 - 2005
Governor of Bank Indonesia and Minister of Finance
Radius Prawiro
1928 - 2005
Governor of Bank Indonesia and Minister of Finance
 Erwin Rommel
1891 - 1944
Military General
Erwin Rommel
1891 - 1944
Military General
 Friedrich Wohler
1800 - 1882
Organic and inorganic chemistry
Friedrich Wohler
1800 - 1882
Organic and inorganic chemistry
 Judith Kerr
1923 - 2019
Children's literature
Judith Kerr
1923 - 2019
Children's literature
 Hans Wilhelm Munch
1911 - 2001
SS physician at Auschwitz concentration camp
Hans Wilhelm Munch
1911 - 2001
SS physician at Auschwitz concentration camp
 Leo Strauss
1899 - 1973
Political philosopher and classical scholar
Leo Strauss
1899 - 1973
Political philosopher and classical scholar
 Manfred Rommel
1928 - 2013
Mayor of Stuttgart
Manfred Rommel
1928 - 2013
Mayor of Stuttgart
 Conrad Veidt
1893 - 1943
Silent film star
Conrad Veidt
1893 - 1943
Silent film star
 Wilhelm II
1859 - 1941
German Emperor and King of Prussia
Wilhelm II
1859 - 1941
German Emperor and King of Prussia
 Nathan Mayer Rothschild
1777 - 1836
Founder of the English branch
Nathan Mayer Rothschild
1777 - 1836
Founder of the English branch
 Rainer Werner Fassbinder
1945 - 1982
Director, actor, and dramatist
Rainer Werner Fassbinder
1945 - 1982
Director, actor, and dramatist
 Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
1770 - 1831
German idealism, dialectical logic
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
1770 - 1831
German idealism, dialectical logic
 Hermann von Helmholtz
1821 - 1894
Scientist and philosopher
Hermann von Helmholtz
1821 - 1894
Scientist and philosopher
 Uta Hagen
1919 - 2004
Actress and theatre practitioner
Uta Hagen
1919 - 2004
Actress and theatre practitioner
 Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim
1486 - 1535
Occult writer, theologian, physician
Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim
1486 - 1535
Occult writer, theologian, physician
 Bernhard Riemann
1826 - 1866
Analysis, number theory, differential geometry
Bernhard Riemann
1826 - 1866
Analysis, number theory, differential geometry
 Carl Orff
1895 - 1982
Composer and music educator
Carl Orff
1895 - 1982
Composer and music educator
 Micha Josef Berdyczewski
1865 - 1921
Writer, Journalist, Scholar
Micha Josef Berdyczewski
1865 - 1921
Writer, Journalist, Scholar
 Ursula Thiess
1924 - 2010
Actress and model
Ursula Thiess
1924 - 2010
Actress and model
 Rosa Luxemburg
1871 - 1919
Marxist theorist, anti-war activist
Rosa Luxemburg
1871 - 1919
Marxist theorist, anti-war activist
 Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
1784 - 1844
Monarch and reformer
Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
1784 - 1844
Monarch and reformer
 Eva Braun
1912 - 1945
Photographer and Adolf Hitler's companion and wife
Eva Braun
1912 - 1945
Photographer and Adolf Hitler's companion and wife
 Heinrich Heine
1797 - 1856
Poet, writer and literary critic
Heinrich Heine
1797 - 1856
Poet, writer and literary critic
 Peter Behrens
1868 - 1940
Architect, graphic and industrial designer
Peter Behrens
1868 - 1940
Architect, graphic and industrial designer
 Baron Munchausen
1720 - 1797
Nobleman and soldier
Baron Munchausen
1720 - 1797
Nobleman and soldier
 Victoria Louise of Prussia
1892 - 1980
Princess of Prussia and Duchess of Brunswick
Victoria Louise of Prussia
1892 - 1980
Princess of Prussia and Duchess of Brunswick
 Hassan Sobhi Mourad
1942 - 2015
Academic
Hassan Sobhi Mourad
1942 - 2015
Academic
 Georg Simon Ohm
1789 - 1854
Physicist and mathematician, known for Ohm's law
Georg Simon Ohm
1789 - 1854
Physicist and mathematician, known for Ohm's law
 Karl Friedrich May
1842 - 1912
Author of travel and adventure stories
Karl Friedrich May
1842 - 1912
Author of travel and adventure stories
 Anahita Ratebzad
1931 - 2014
Politician, Physician
Anahita Ratebzad
1931 - 2014
Politician, Physician
 Frederick William
1620 - 1688
Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia
Frederick William
1620 - 1688
Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia
 Henry Brandon
1912 - 1990
Character actor
Henry Brandon
1912 - 1990
Character actor
 Lutz Graf Schwerin von Krosigk
1887 - 1977
Finance minister of Germany
Lutz Graf Schwerin von Krosigk
1887 - 1977
Finance minister of Germany
 Clara Wieck Schumann
1819 - 1896
Pianist, composer, and piano teacher
Clara Wieck Schumann
1819 - 1896
Pianist, composer, and piano teacher
 Karen Horney
1885 - 1952
Psychoanalyst and feminist theorist
Karen Horney
1885 - 1952
Psychoanalyst and feminist theorist
 Monika Dannemann
1945 - 1996
Figure skater and painter
Monika Dannemann
1945 - 1996
Figure skater and painter
 Ludovika Wilhelmine of Bavaria
1808 - 1892
Princess of Bavaria
Ludovika Wilhelmine of Bavaria
1808 - 1892
Princess of Bavaria
 Caspar David Friedrich
1774 - 1840
Romantic landscape painter
Caspar David Friedrich
1774 - 1840
Romantic landscape painter
 Moses Mendelssohn
1729 - 1786
Philosopher and theologian
Moses Mendelssohn
1729 - 1786
Philosopher and theologian
 Max Born
1882 - 1970
Quantum mechanics pioneer
Max Born
1882 - 1970
Quantum mechanics pioneer
 Friedrich Froebel
1782 - 1852
Founder of kindergarten and educational theorist
Friedrich Froebel
1782 - 1852
Founder of kindergarten and educational theorist
 Diem Brown
1980 - 2014
Reality television personality
Diem Brown
1980 - 2014
Reality television personality
 Ludwig Feuerbach
1804 - 1872
Philosopher and anthropologist
Ludwig Feuerbach
1804 - 1872
Philosopher and anthropologist
 Leo von Klenze
1784 - 1864
Neoclassical architect and painter
Leo von Klenze
1784 - 1864
Neoclassical architect and painter
 Helmut Kohl
1930 - 2017
Chancellor of Germany
Helmut Kohl
1930 - 2017
Chancellor of Germany
 Balthasar Neumann
1687 - 1753
Baroque architecture
Balthasar Neumann
1687 - 1753
Baroque architecture
 Hermann Ebbinghaus
1850 - 1909
Experimental study of memory
Hermann Ebbinghaus
1850 - 1909
Experimental study of memory
 Frederick William II of Prussia
1744 - 1797
King of Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg
Frederick William II of Prussia
1744 - 1797
King of Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg
 Jenny von Westphalen
1814 - 1881
Theatre critic and political activist
Jenny von Westphalen
1814 - 1881
Theatre critic and political activist
 Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi
1804 - 1851
Mathematician
Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi
1804 - 1851
Mathematician
 Ludwig Erhard
1897 - 1977
Economist and statesman
Ludwig Erhard
1897 - 1977
Economist and statesman
 Isang Yun
1917 - 1995
Composer of avant-garde music
Isang Yun
1917 - 1995
Composer of avant-garde music
 Mohammad Yusuf Khan
1917 - 1998
Prime Minister of Afghanistan
Mohammad Yusuf Khan
1917 - 1998
Prime Minister of Afghanistan
 Karl Marx
1818 - 1883
Revolutionary socialist, historian
Karl Marx
1818 - 1883
Revolutionary socialist, historian
 Ludwig Mies van der Rohe
1886 - 1969
Architect and educator
Ludwig Mies van der Rohe
1886 - 1969
Architect and educator
 Max Weber
1864 - 1920
sociologist
Max Weber
1864 - 1920
sociologist
 Willem Frederik
1772 - 1843
the first King of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Willem Frederik
1772 - 1843
the first King of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
 Louise of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg
1800 - 1831
Duchess consort of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld
Louise of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg
1800 - 1831
Duchess consort of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld
 Sibylle Bergemann
1941 - 2010
Photographer
Sibylle Bergemann
1941 - 2010
Photographer
 Stefan Askenase
1896 - 1985
Classical pianist and pedagogue
Stefan Askenase
1896 - 1985
Classical pianist and pedagogue
 Herbert Marcuse
1898 - 1979
Political philosopher and social theorist
Herbert Marcuse
1898 - 1979
Political philosopher and social theorist
 Johann Conrad Schlaun
1695 - 1773
Architect of the Westphalian Baroque style
Johann Conrad Schlaun
1695 - 1773
Architect of the Westphalian Baroque style
 Klaus Nomi
1944 - 1983
New wave synthpop opera experimental baroque
Klaus Nomi
1944 - 1983
New wave synthpop opera experimental baroque
 Harald Quandt
1921 - 1967
Industrialist
Harald Quandt
1921 - 1967
Industrialist
 Felix Christian Klein
1849 - 1925
Mathematics professor and educator
Felix Christian Klein
1849 - 1925
Mathematics professor and educator
 Ignatius Zakka I
1933 - 2014
Patriarch of Antioch and head
Ignatius Zakka I
1933 - 2014
Patriarch of Antioch and head
 Hermann Biow
1804 - 1850
Daguerreotypist
Hermann Biow
1804 - 1850
Daguerreotypist
 August Kekule
1829 - 1896
Organic chemist
August Kekule
1829 - 1896
Organic chemist
 Henry IV
1050 - 1106
Holy Roman Emperor and King of Germany
Henry IV
1050 - 1106
Holy Roman Emperor and King of Germany
 Anne Frank
1929 - 1945
Diarist
Anne Frank
1929 - 1945
Diarist
 Samuel Hahnemann
1755 - 1843
Founder of homeopathy
Samuel Hahnemann
1755 - 1843
Founder of homeopathy
 Michael Klein
1959 - 1993
Footballer
Michael Klein
1959 - 1993
Footballer
 Gottlieb Daimler
1834 - 1900
Engineer, industrialist, automotive pioneer
Gottlieb Daimler
1834 - 1900
Engineer, industrialist, automotive pioneer
 Kabir Stori
1942 - 2006
Writer, Poet
Kabir Stori
1942 - 2006
Writer, Poet
 Johann Pachelbel
1653 - 1706
Composer and organist
Johann Pachelbel
1653 - 1706
Composer and organist
 Hugo Ferdinand Boss
1885 - 1948
Founder of Hugo Boss AG
Hugo Ferdinand Boss
1885 - 1948
Founder of Hugo Boss AG
 Fanny Mendelssohn
1805 - 1847
Composer and pianist of the early Romantic era
Fanny Mendelssohn
1805 - 1847
Composer and pianist of the early Romantic era
 George Frideric Handel
1685 - 1759
composer
George Frideric Handel
1685 - 1759
composer
 Sophie Scholl
1921 - 1943
Anti-Nazi political activist
Sophie Scholl
1921 - 1943
Anti-Nazi political activist
 Rob Pilatus
1965 - 1998
Member of Milli Vanilli
Rob Pilatus
1965 - 1998
Member of Milli Vanilli
 George Muller
1805 - 1898
Christian evangelist and director of the Ashley
George Muller
1805 - 1898
Christian evangelist and director of the Ashley
 Curd Jurgens
1915 - 1982
Film and stage actor
Curd Jurgens
1915 - 1982
Film and stage actor
 Alexandra Feodorovna
1872 - 1918
Empress consort of Russia
Alexandra Feodorovna
1872 - 1918
Empress consort of Russia
 Christian Leden
1882 - 1957
Ethnomusicologist and explorer
Christian Leden
1882 - 1957
Ethnomusicologist and explorer
 Bert Kaempfert
1923 - 1980
Orchestra leader, music producer
Bert Kaempfert
1923 - 1980
Orchestra leader, music producer
 Adelaide of Saxe-Meiningen
1792 - 1849
Queen consort of the United Kingdom and Hanover
Adelaide of Saxe-Meiningen
1792 - 1849
Queen consort of the United Kingdom and Hanover
 Rikard Nordraak
1842 - 1866
Composer of the Norwegian national anthem
Rikard Nordraak
1842 - 1866
Composer of the Norwegian national anthem
 Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel
1834 - 1919
Zoologist and evolutionist
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel
1834 - 1919
Zoologist and evolutionist
 Carl Laemmle
1867 - 1939
Film producer and co-founder of Universal Pictures
Carl Laemmle
1867 - 1939
Film producer and co-founder of Universal Pictures
 Joseph Beuys
1921 - 1986
Sculptor and performance artist
Joseph Beuys
1921 - 1986
Sculptor and performance artist
 Otto Lilienthal
1848 - 1896
Engineer and glider pilot
Otto Lilienthal
1848 - 1896
Engineer and glider pilot
 Francisco Andrade
1856 - 1921
Opera singer
Francisco Andrade
1856 - 1921
Opera singer
 George Grosz
1893 - 1959
Painter, caricaturist, satirist
George Grosz
1893 - 1959
Painter, caricaturist, satirist
 Max Planck
1858 - 1947
Quantum theory
Max Planck
1858 - 1947
Quantum theory
 Tahseen Said
1933 - 2019
Hereditary leader of Yazidis and head
Tahseen Said
1933 - 2019
Hereditary leader of Yazidis and head
 Marwan Kassab-Bachi
1934 - 2016
Painter
Marwan Kassab-Bachi
1934 - 2016
Painter
 Johann Sebastian Bach
1685 - 1750
Baroque composer and organist
Johann Sebastian Bach
1685 - 1750
Baroque composer and organist
 Elizabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate
1652 - 1722
Correspondent and memoirist
Elizabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate
1652 - 1722
Correspondent and memoirist
 Yehudi Menuhin
1916 - 1999
violinist and conductor
Yehudi Menuhin
1916 - 1999
violinist and conductor
 William Herschel
1738 - 1822
Founder of sidereal astronomy
William Herschel
1738 - 1822
Founder of sidereal astronomy
 Justus von Liebig
1803 - 1873
Chemist and agricultural scientist
Justus von Liebig
1803 - 1873
Chemist and agricultural scientist
 Johannes Gutenberg
1400 - 1468
Inventor of the printing press and movable type
Johannes Gutenberg
1400 - 1468
Inventor of the printing press and movable type
 Karl Friedrich Otto Wolff
1900 - 1984
Chief of Personal Staff Reichsführer-SS
Karl Friedrich Otto Wolff
1900 - 1984
Chief of Personal Staff Reichsführer-SS
 Wojciech Dlugoraj
1557 - 1619
Renaissance composer and lutenist
Wojciech Dlugoraj
1557 - 1619
Renaissance composer and lutenist
 Jacques Offenbach
1819 - 1880
Operetta pioneer
Jacques Offenbach
1819 - 1880
Operetta pioneer
 Kurt Julian Weill
1900 - 1950
Composer for the stage and concert hall
Kurt Julian Weill
1900 - 1950
Composer for the stage and concert hall
 Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg
1868 - 1914
Wife of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria
Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg
1868 - 1914
Wife of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria
 Erich Johann Albert Raeder
1876 - 1960
Commander-in-chief of the Kriegsmarine
Erich Johann Albert Raeder
1876 - 1960
Commander-in-chief of the Kriegsmarine
 Karl Lagerfeld
1933 - 2019
Creative director of Chanel and Fendi
Karl Lagerfeld
1933 - 2019
Creative director of Chanel and Fendi
 Birol Unel
1961 - 2020
Actor
Birol Unel
1961 - 2020
Actor
 Romeo Sabourin
1923 - 1944
Spy
Romeo Sabourin
1923 - 1944
Spy
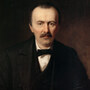 Heinrich Schliemann
1822 - 1890
Archaeological excavator of Troy, Mycenae
Heinrich Schliemann
1822 - 1890
Archaeological excavator of Troy, Mycenae
 Nico
1938 - 1988
Singer, songwriter, actress and model
Nico
1938 - 1988
Singer, songwriter, actress and model
 Friedrich Ebert
1871 - 1925
Leader of the Social Democratic Party of Germany
Friedrich Ebert
1871 - 1925
Leader of the Social Democratic Party of Germany
 Otto Hahn
1879 - 1968
Chemist and pioneer of radioactivity
Otto Hahn
1879 - 1968
Chemist and pioneer of radioactivity
 Frederick III
1831 - 1888
German Emperor and King of Prussia
Frederick III
1831 - 1888
German Emperor and King of Prussia
 Primoz Trubar
1508 - 1586
Protestant Reformer
Primoz Trubar
1508 - 1586
Protestant Reformer
 Friedrich Wilhelm von Steuben
1730 - 1794
Inspector General
Friedrich Wilhelm von Steuben
1730 - 1794
Inspector General
 Helmut Newton
1920 - 2004
Fashion photographer
Helmut Newton
1920 - 2004
Fashion photographer
 Alexandra Louise Olga Victoria of Saxe
1878 - 1942
Princess consort of Hohenlohe-Langenburg
Alexandra Louise Olga Victoria of Saxe
1878 - 1942
Princess consort of Hohenlohe-Langenburg
 Jakob Savinsek
1922 - 1961
Sculptor
Jakob Savinsek
1922 - 1961
Sculptor
We Need -- admin in